设计思想
Redux 的设计思想很简单,就两句话。
1. Web 应用是一个状态机,视图与状态是一一对应的。
2. 所有的状态,保存在一个对象里面。基本概念和API
Store
Store 就是保存数据的地方,你可以把它看成是一个容器。整个应用只能有一个Store。Redux 提供createStore 这个函数,用来生成Store。
1 | import { createStore } from 'redux'; |
Redux 规定,一个State 对应一个View。只要State 相同,View 相同。你知道State,就知道View 是什么样,反之亦然。
Action
State 的变化,会导致View 的变化。但是,用户接触不到State,只能接触到View。所以,State 的变化必须是View 导致的。
Action 就是View 发出的通知,表示State 应该要发生变化了。Action 是一个对象。其中的type 属性是必须的,表示Action 的名称。其他属性可以自由设置,社区有一个规范https://github.com/acdlite/flux-standard-action 可以参考。
1 | const action = { |
上面代码中,Action 的名称是ADD_TODO,它携带的信息是字符串Learn Redux。可以这样理解,Action 描述当前发生的事情。改变State 的唯一方法,就是使用Action。它会运送数据到Store。
Action Creator
View 要发送多少种消息,就会有多少种Action。如果都手写,会很麻烦。可以定义一个函数来生成Action,这个函数就叫Action Creator。
1 | const ADD_TODO = '添加 TODO'; |
上面代码中,addTodo 函数就是一个Action Creator
store.dispatch()
store.dispatch() 是View 发出Action 的唯一方法。
1 | import { createStore } from 'redux'; |
上面代码中,store.dispatch 接受一个Action 对象作为参数,将它发送出去。结合Action Creator,这段代码可以改写如下。
1 | store.dispatch(addTodo('Learn Redux')); |
Reducer
Store 收到Action 以后,必须给出一个新的State,这样View 才会发生变化。这种State 的计算过程就叫做Reducer。Reducer 是一个函数,它接受Action 和当前State 作为参数,返回一个新的State。
1 | const reducer = function(state, action){ |
整个应用的初始状态,可以作为State 的默认值。下面是一个实际的例子
1 | const defaultState = 0; |
上面代码中,reducer 函数收到名为ADD 的Action 以后,就返回一个新的State,作为加法的计算结果。其他运算的逻辑(比如减法),也可以根据Action 的不同来实现。
实际应用,Reducer 函数不用像上面这样手动调用,store.dispatch 方法会触发Reducer 的自动执行。为此,Store 需要知道Reducer 函数,做法就是在生成Store 的时候,将Reducer 传入createStore 方法。
1 | import { createStore } from 'redux'; |
上面代码中,createStore 接受Reducer 作为参数,生成一个新的Store。以后每当store.dispatch 发送过来一个新的Action,就会自动调用Reducer ,得到新的State。
为什么这个函数叫做Reducer 呢?因为它可以作为数组的reducer 方法的参数。请看下面的例子,一系列Action 对象按照顺序作为一个数组。
1 | const actions = [ |
上面代码中,数组actions 表示依次有三个Action,分别是加0、加1 和加2。数组的reduce 方法接受Reducer 函数作为参数,就可以直接得到最终的状态3。
纯函数
Reducer 函数最重要的特征是,它是一个纯函数。也就是说,只要是同样的输入,必定得到同样的输出。纯函数是函数式编程的概念,必须遵守一下一些约束。
* 不得改写参数
* 不能调用系统I/O 的API
* 不能调用Date.now() 或者Math.random() 等不纯的方法,因为每次会得到不一样的结果由于Reducer 是纯函数,就可以保证同样的State,必定得到同样的View。当也正因为这一点,Reducer 函数里面不能改变State,必须返回一个全新的对象,请参考下面的写法。
1 | // State 是一个对象 |
最好把State 对象设成只读。你没法改变它,要得到新的State,唯一办法就是生成一个新对象。这样的好处是,任何时候,与某个View 对应的State 总是一个不变的对象。
store.subscribe()
Store 允许使用store.subscribe 方法设置监听函数,一旦State 发生变化,就自动执行这个函数。
1 | import { createStore } from 'redux'; |
显然,只要把View 的更新函数(对于React 项目,就是组件的render 方法或setState、 方法)放入listen,就会实现View 的自动渲染。
store.subscribe 方法返回一个函数,调用这个函数就可以解除监听。
1 | let unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => |
Store 的实现
上一节介绍了Redux 涉及的基本概念,可以发现Store 提供了三个方法。
* store.getState()
* store.dispatch()
* store.subscribe()
1 | import { createStore } from 'redux'; |
createStore 方法还可以接受第二个参数,表示state 的最初状态。这通常是服务器给出的。
1 | let store = createStore(todoApp, window.STATE_FROM_SERVER) |
上面代码中,window.STATE_FROM_SERVER 就是整个应用的初始值。注意,如果提供了这个按时,它会覆盖Reducer 函数的默认初始值。
下面是createStore 方法的一个简单实现,可以了解一下Store 是怎样生成的。
1 | const createStore = (reducer) => { |
Reducer 的拆分
Reducer 函数负责生成State。由于整个应用只有一个State 对象,包含所有数据,对于大型应用来说,这个State 必然十分庞大,导致Reducer 函数也十分庞大。
1 | const chatReducer = ( state = defaultState, action = {}) => { |
上面代码中,三种Action 分别改变State 的三个属性。
1 |
|
上面代码中,Reducer 函数被拆分成了三个小函数,每一个负责生成对应的属性。
这样一拆,Reducer 就易读写多了。而且,这种拆分与React 应用的结构相吻合:一个React 根组件由很多子组件构成。这就是说,子组件与子Reducer 完全可以对应。
Redux 提供了一个combineReducers 方法,用于Reducer 的拆分。你只要定义刚刚子Reducer 函数,然后用这个方法,将它们合成一个大的Reducer。
1 | import { combineReducer } from 'redux'; |
上面的代码通过combineReducers 方法将三个子Reducer 合并成一个大的函数。
这种写法有一个前提,就是State 的属性名必须与子Reducer 同名。如果不同名,就要采用下面的写法。
1 | const reuder = combineReducer({ |
总之,combineReducers() 做的就是产生一个整体的Reducer 函数。该函数根据state 的key 去执行响应的子Reducer,并将返回结果合并成一个大的State 对象。
下面是 combineReducers 的简单实现
1 | const combineReducers = reducers => { |
你可以把所有子Reducer 放在一个文件里面,然后统一引入。
1 | import { combineReducers } from 'redux' |
工作流程
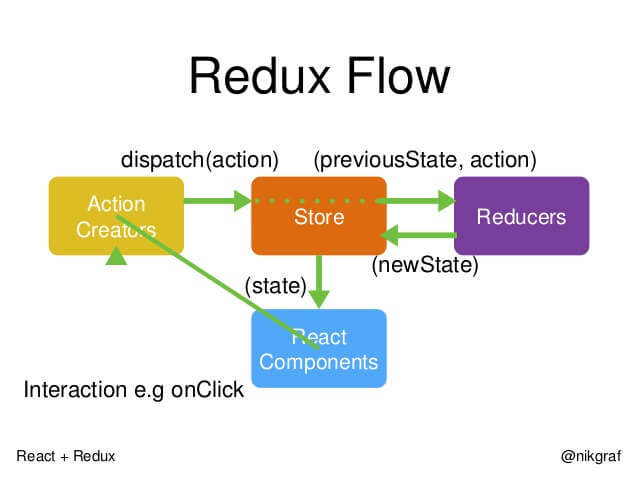
首先,用户发出Action
1 | store.dispatch(action); |
然后,Store 自动调用Reducer,并且传两个参数:当前State 和收到的Action。Reducer 会返回新的State。
1 | store.dispatch(action); |
State 一旦有变化,Store 就会调用监听函数。
1 | // 设置监听函数 |
listener 可以通过store.getState() 得到当前状态。如果使用的是React,这是可以触发重新渲染View。
1 | function listener(){ |